April 20th, 2015
Association for the Advancement of Medical Instrumentation
4301 N Fairfax Drive Suite 301
Arlington, VA 22203-1633 USA
RE: Current FDA Resistance Requirements for Steam Biological Indicators Used in Validation
Dear AAMI,
In recent conversations with FDA, we became aware that there are now different requirements for the resistance characteristics (D-value and Z-value) of steam biological indicators being used in reusable medical device efficacy validations than those commonly being used and accepted by the medical industry. Such a change has the potential to cause significant issues for not only medical device manufacturers but also the validation laboratories performing studies on their behalf.
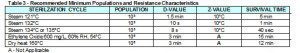
Specifically, the FDA is now requiring biological indicators used in steam validation studies to match the minimum resistance requirements of healthcare BI’s as identified in the FDA guidance document entitled “Guidance for Industry and FDA Staff Biological Indicator (BI) Premarket Notification [510(k)] Submissions”. The FDA is referring to Table 3 in the guidance document, which list the minimum requirements for BI’s used to monitor routine steam sterilization cycles in healthcare facilities at various sterilization temperatures. Please see Table 3 below for your review.
Table 3 – Recommended Minimum Populations and Resistance Characteristics
In our opinion, Table 3 was not created to be applied to steam biological indicators used in the sterilization efficacy validations of reusable medical devices. The guidance document issued on October 4th, 2007 is meant for biological indicator manufacturers trying to secure clearance for their healthcare biological indicators. We have AAMI and ISO standards which provide guidance for the use of biological indicators to be used in medical device validations.
The resistance characteristics in Table 3 typically apply to self-contained biological indicators which are primarily used throughout healthcare. Steam self-contained biological indicators have filters, small access holes and are encapsulated within plastic housings, which make it more difficult for the steam molecules to reach the spore strips located at the bottom of the self-contained BI’s vial. This torturous path adds to the resistance characteristics of healthcare biological indicators. However, in steam validation work, we typically use “naked BI’s” such as spore strips, inoculated wires, threads, coupons or spore suspension directly inoculated on devices. It will be nearly impossible for biological indicator manufacturers to make these type of validation BI’s as resistant as the characteristics the FDA is requiring for healthcare BI’s at temperature of 132°C-135°C.
Two actual steam BI’s considered to be very resistant based on their 121°C D-values are shown below. Example 1 is a 106 spore strip and example 2 is a suspension. Both have 121°C D-values greater than 2.0 minutes, but after reviewing their resistance data at 132°C, neither meet the FDA’s healthcare biological indicator requirement for a D-value of no less than 10 seconds at 132°C.
1. 106 Spore Strip with a 121°C D-value of 2.5 minutes (132.2°C D-value is 6.6 seconds)
2. 106 Suspension with a 121°C D-value of 2.1 minutes (132.2°C D-value is 6.7 seconds)
If the FDA requires compliance of the resistance characteristics of biological indicators used in steam validation to equal those of biological indicators used in healthcare at temperatures such as 132-135°C, it can cause major issues for device manufacturers trying to validate their products in steam sterilization cycles.
To clarify even further, we can apply the Fbio formula to various BI’s at 121°C in order to compare individual BI resistance characteristics. The Fbio formula is as follows; Fbio = log (initial population) x D value
Below are the calculations and a Table depicting the minimum resistance characteristics of a validation BI, a healthcare BI and BI examples 1 and 2 as have been shown above:
Validation BI:
Spore population = 1 x 106
D value = 1.0 minutes
Fbio = log (initial population) x D value
= 106 x 1.0
= 6 x 1
= 6
Healthcare BI:
Spore population = 1 x 105
D value = 1.5 minutes
Fbio = log (initial population) x D value
= log 105 x 1.5
= 5 x 1.5
= 7.5
Example 1 BI:
Spore population = 1 x 106
D value = 2.5 minutes
Fbio = log (initial population) x D value
= 106 x 1.5
= 6 x 2.5
= 15.0
Example 2 BI:
Spore population = 1 x 106
D value = 2.1 minutes
Fbio = log (initial population) x D value
= 106 x 1.5
= 6 x 2.1
= 12.6
Comparison Table of Resistance Characteristics of Various BI’s
The Table above shows that BI’s 1 and 2 are not only extremely resistant BI’s but that they also have significantly higher Fbio’s than are now required for steam sterilization efficacy validation work. However, if the FDA continues on this path, neither would be accepted for use if validating instruments in steam sterilization cycles running at 132-135°C.
With all the progress made to reduce extended steam cycles in healthcare facilities, the results of steam validations using biological indicators with healthcare BI resistance characteristics may end up creating the same cycles we have tried to eliminate for years. If pursued by the FDA, this change would affect the medical device industry as a whole and therefore, we felt obligated to bring this issue to your attention in the hope that we may be able to discuss it at the upcoming AAMI Spring meetings.
Respectfully Submitted,
Gary J. Socola
President
HIGHPOWER Validation Testing & Lab Services Inc.